Those suffering from alcohol addiction who want to undergo detox and treatment should understand how withdrawal symptoms impact the body. Withdrawal symptoms are more common the longer someone has been drinking. Other factors also impact what symptoms an alcoholic may experience during detox or treatment. An inpatient detox or treatment center for alcoholism consists of a team of medical professionals and mental health professionals to help those suffering from alcoholism follow through with their detox despite withdrawal.
What Are the Symptoms of Alcohol Withdrawal?

Symptoms of withdrawal can make the road to recovery a challenge for those suffering from alcoholism. The type and severity of withdrawal symptoms will depend on how much alcohol a person tends to drink and how long they’ve been drinking heavily. Addicts who have been drinking longer will likely experience more withdrawal symptoms.
Sleep Disturbance and Restlessness
Alcohol can help a person fall asleep, but it reduces the quality of their sleep. When someone stops drinking, their hyperactive CNS may make it difficult for them to fall asleep and mean that when they do sleep, it’s restless and fitful. An elevated heart rate, excessive sweating and increased blood pressure are all common side effects and can contribute to poor sleep. Fortunately, in milder cases of withdrawal, these symptoms pass quickly.
Nausea and Vomiting
Long-term alcohol use causes damage to the stomach lining. However, drinking alcohol temporarily soothes that damaged stomach lining. When a person stops drinking alcohol cold turkey, they’ll likely feel nauseated and may struggle to hold down food. The stomach lining will repair itself over time, but these acute symptoms can be unpleasant.
Heachaches
When someone stops drinking alcohol, they may experience headaches and other related symptoms such as sensitivity to light. In some cases, the headaches are caused by dehydration and electrolyte imbalances. In others, it’s a symptom of the CNS struggling to adapt to the lack of alcohol. Proper hydration is essential during this time, and it may also help to spend time in a calm, quiet space.
Delirium Tremens

One of the most severe alcohol withdrawal symptoms is delirium tremens. This condition usually starts about three days into withdrawal, and the symptoms usually last just a few days. Mild delirium tremens symptoms can include:
- Shakes
- Confusion
- Hallucinations
In cases with severe symptoms, the sufferer may experience convulsions, seizures and other serious medical complications. Without medical intervention, these symptoms can have severe consequences, either in the form of lasting complications or death.
When Does Alcohol Withdrawal Start?
Alcohol withdrawal symptoms may start at different times based on how much alcohol someone intakes and how frequently. However, there is a general timeline that can provide insight into the average start time to prepare for alcohol withdrawal symptoms.
Alcohol withdrawal typically begins around 6 hours after cessation or decrease in intake. Detox is best done in the safety of a detox program, where those suffering from alcoholism have medical health professionals and other resources there when needed.
How Long Does Alcohol Withdrawal Last?

Alcohol withdrawal typically lasts 1-2 weeks, though post-acute withdrawal symptoms (PAWS) may last several weeks or even months. Mild to moderate withdrawal symptoms begin in the first 6-12 hours. These peak between 24-72 hours. During this time, addicts may experience hallucinations, anxiety, fatigue, and even acute symptomatic seizures.
Severe withdrawal symptoms, including delirium tremens, begin 48-72 hours after the last drink. This peaks around 2-4 days into detox.
All throughout the detox, those suffering from alcohol addiction may experience mental health struggles alongside health issues. This includes anxiety, cravings for alcohol, and mood swings. When taking part in a detox program or other treatment program, mental health professionals use therapeutic modalities to help those suffering from alcohol abuse on their road to recovery.
What Helps with Alcohol Withdrawal?
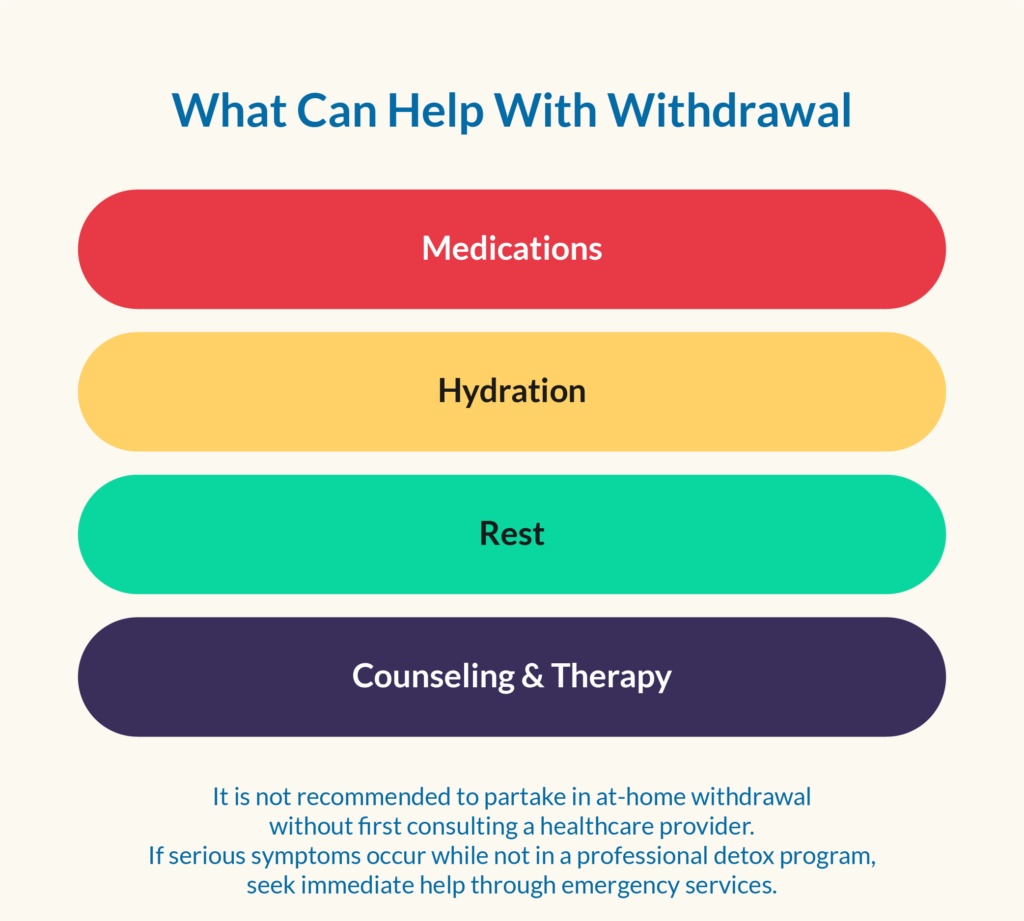
Alcohol withdrawal can be challenging for anyone, whether they experience mild to moderate or severe symptoms. During treatment, several factors help alleviate withdrawal symptoms including:
- Medications: in detox programs, medical professionals on staff may help administer medications to those suffering serious withdrawal symptoms
- Hydration: staying hydrated helps alleviate some physical symptoms of withdrawal. Severe dehydration, which can become life-threatening, occurs due to vomiting, sweating, or lack of proper hydration
- Rest: sleep disturbances are a common withdrawal symptoms, but resting when possible will help get through the recovery process
- Counseling and therapy: cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) and other counseling methods can address underlying issues related to alcohol use.
If serious withdrawal symptoms occur when not in a professional detox program, seek immediate help from emergency services. This includes serious forms of Delirium Tremens (DTs). It is not recommended to partake in an at-home withdrawal without first consulting with a healthcare provider.
Can You Die from Alcohol Withdrawal?
While fatalities from alcohol withdrawal are uncommon, they are still possible. Delirium Tremens (DTs) occurs in about 3-5% of addicts going through withdrawal. Untreated puts those going through DTs at serious risk. Medical care drops the life-threatening risk significantly. Another life-threatening condition that occurs during withdrawal are seizures. Multiple seizures or prolonged ones can put someone at risk of serious health problems.
Severe dehydration can cause organ failure during withdrawal. Vomiting is a common symptom for those undergoing alcohol withdrawal. Sweating is also common. Ensuring that you are properly hydrated throughout withdrawal reduces the risk of organ failure or other symptoms of dehydration.
Lastly, increases in blood pressure and heart rate can lead to heart attacks or strokes. Heart disease can also result from persistent alcohol abuse.
If any risks of fatality are present during detox, hospitalization may be more effective than a treatment center. Emergency services should always be contacted for the above symptoms.









